- Home
- Facilities
Drishti Eye Care & Research Centre
Fluorescein Angiography
Fluorescent Angiography (FAG) is a technique for examining the circulation of the retina and choroid using a fluorescent dye and a specialized camera. fluorescein angiography(Digital) to diagnose retinal abnormalities can now be diagnosed and treated in the same visit.

Retinal Laser
Lasers are machines that amplify light rays to the point where they can be useful for many different applications. In eye surgery, laser can be used for many different reasons, including treating:
- Retinal conditions (such as retinal tears, diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusions)
- Short or Long-Sightedness
- Patients for after-cataract
YAG Laser
After cataract surgery, the cataract will never come back. However there is a chance that a protein film will form across the posterior capsule. This protein material is generated from microscopic cells that cling to the anterior capsule and the equator of the natural lens which became a cataract. The YAG (Yttrium-Aluminum Garnet) laser uses laser light in a focused beam to make small openings in the posterior capsule to clear the clouded membrane. No anesthetic is required since the capsule has no nerve endings and therefore there is no pain, just like hair or finger nails can be cut without pain.

Visual Field Analysis
A perimetry test (visual field test) is a method of measuring an individual’s entire scope of vision, that is their central and peripheral (side) vision. Visual field testing actually maps the visual fields of each eye individually. It can help find certain patterns of vision loss. This may mean a certain type of eye disease is present.
It is a good test to find vision loss caused by the eye disease- glaucoma. Regular perimetry tests can be used to see if treatment for glaucoma is preventing further vision loss.
The amount of peripheral vision loss is linked to the amount of optic nerve damage.In addition, visual field tests are useful for detection of central or peripheral retinal disease, eyelid conditions such as ptosis or drooping, optic nerve disease, and diseases affecting the visual pathways within the brain. This test is conducted by our optometrist and interpreted by the eye doctor.

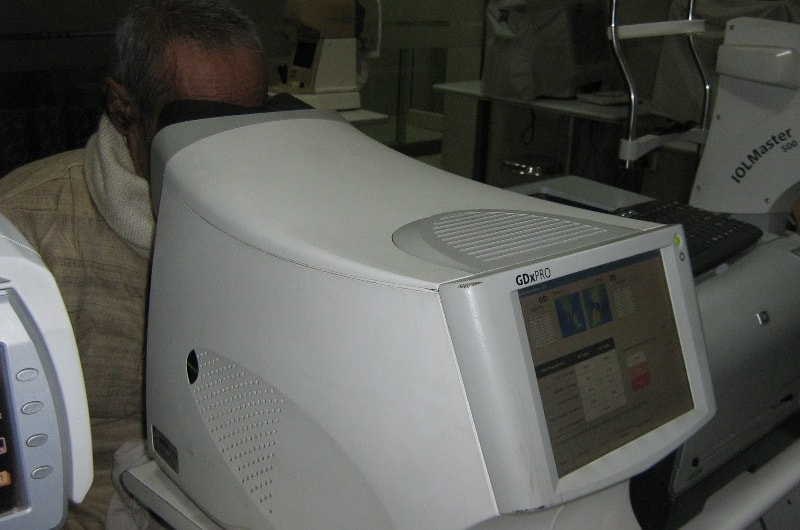
ONH Analyser/RNFL
A patient may present with optic nerves/RNFLs that are suspicious for glaucoma but may have full visual fields. The clinician must determine whether the advanced imaging technology is detecting early glaucoma or if the optic nerve is normal with some features associated with glaucoma. Structural changes can precede functional ones. In early glaucoma, Only the optic nerve/RFNL may be affected, and the OCT may identify the compromise.

A/B Ultrasonography
1. A-Scan
A-scan is an amplitude modulation scan. It gives the information in the form of one dimensional. it is used to detect the presence of flaws in the materials. A-scan ultrasound biometry, commonly referred to as an A-scan, is routine type of diagnostic test used in ophthalmology. The A-scan provides data on the length of the eye, which is a major determinant in common sight disorders. The most common use of the A-scan is to determine eye length for calculation of intraocular lens power. Briefly, the total refractive power of the emmetropic eye is approximately 60. Of this power, the cornea provides roughly 40 diopters, and the crystalline lens 20 diopters. When a cataract is removed, the lens is replaced by an artificial lens implant. By measuring both the length of the eye (A-scan) and the power of the cornea (keratometry), a simple formula can be used to calculate the power of the intraocular lens needed. There are several different formulas that can be used depending on the actual characteristics of the eye.
The other major use of the A-scan is to determine the size and ultrasound characteristics of masses in the eye, in order to determine the type of mass. This is often termed quantitative A-scan.
Instruments used in this type of test require direct contact with the cornea, however a non-contact instrument has been reported. Disposable covers, which come in actual contact with the eye, have also been evaluated.
2. B-Scan
B-scan Ultrasonography, or B-scan, is a diagnostic test used in optometry and ophthalmology to produce a two-dimensional, cross-sectional view of the eye and the orbit. It is otherwise called brightness scan.

Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy is a type of ultrasound eye exam that makes a more detailed image than regular ultrasound. High-energy sound waves are bounced off the inside of the eye and the echo patterns are shown on the screen of an ultrasound machine. This makes a picture called a sonogram. It is useful in glaucoma, cysts and neoplasms of the eye, as well as the evaluation of trauma and foreign bodies of the eye.
OCT (ANT & POST)
Optical Coherence Tomography scan (commonly referred to as an OCT scan) is the latest advancement in imaging technology. Similar to ultrasound, this diagnostic technique employs light rather than sound waves to achieve higher resolution pictures of the structural layers of the back of the eye.

Specular Microscopy
Specular microscopy is a noninvasive photographic technique that facilitates rapid and accurate diagnosis of corneal endotheliopathies.
Specular microscopy can provide a non-invasive morphological analysis of the corneal endothelial cell layer from subjects enrolled in clinical trials. The analysis provides a measure of the endothelial cell physiological reserve from aging, ocular surgical procedures, pharmaceutical exposure, and general health of the corneal endothelium. The purpose of this review is to discuss normal and stressed endothelial cell morphology, the techniques for determining the morphology parameters, and clinical trial applications.
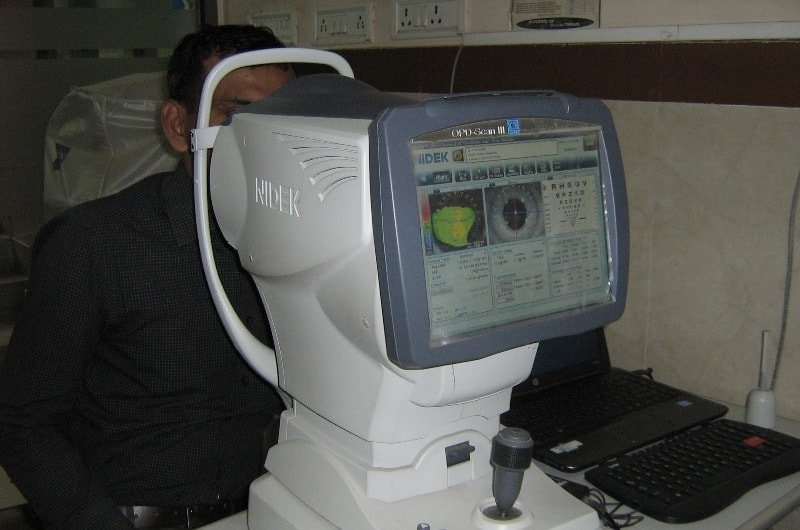
OPD Scan III
OPD Scan III combines three advanced technologies - plus wavefront analysis - in one easy-to-use refractive diagnostic workstation to evaluate your patient comprehensively.
- Wavefront Aberrometer
- Topographer
- Auto Refractometer
- Auto Keratometer
- Pupillometer and Pupillographer
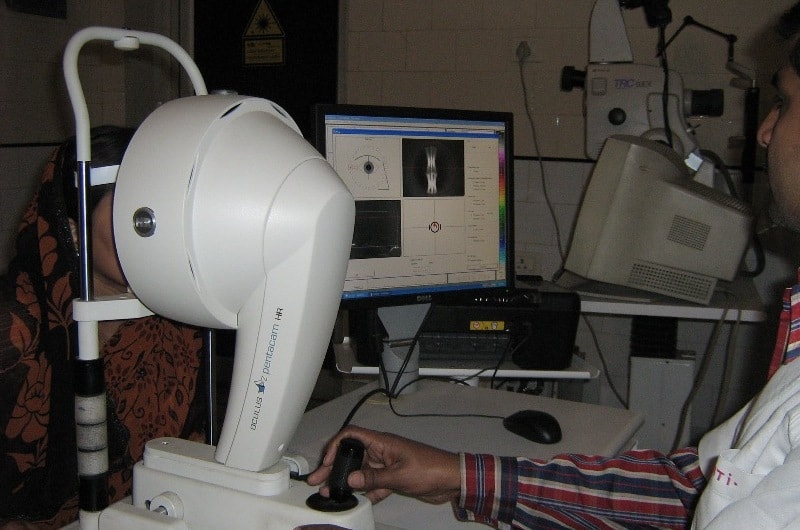
Pentacam
The Pentacam Comprehensive Eye Scanner is a rotating camera that photographs both the anterior (front) and posterior (back) is that it provides more precise measurements of the central cornea than any other ocular surfaces and other areas of the cornea (the front part of the eye). The Pentacam Scanner’s main advantage is that it provides more precise measurements of the central cornea than any other ocular measurement instrument currently available.